In Year 7 Data Representation, you…
- Explored how sequences of symbols can represent information
- Discussed that the symbols used in computing to represent information are 0 and 1, i.e. the binary digits
- Examined how sequences of binary digits can be used to represent letters and numbers
In this topic, you will…
- Examine how sequences of binary digits can be used to represent images and sounds
- Use software tools to experiment with images and sounds
🎯 Learning Objectives
- Create images out of individual coloured elements
- Explore how such an image can correspond to a sequence of binary digits and vice versa
- Define key terms relating to digital image representation
Starter Activity – Going audiovisual

- Open a new Word document with the title Digital Media Lesson 1.
- Then under a subtitle of Starter Activity answer the question below:
- How are images and sounds represented in digital devices?
- Then answer the two questions below.
What are these symbols called?
000101101111000100010110110110101010101000101011What are they used for in computing?
🥇 Level 1 – Binary Mosaic
Download the activity below and follow the steps listed here and given by your teacher.
Step 1 – Create a picture from individual elements
You can:
- Use up to four different colours
You cannot:
- Leave picture elements without a colour
- Use more than one colour in an element
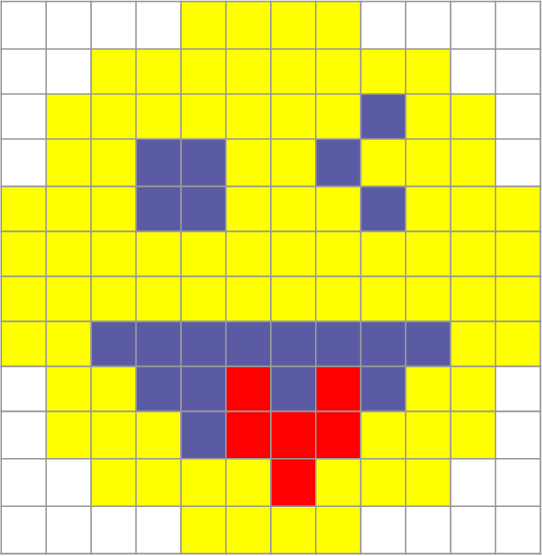
Step 2 – Use one or two binary digits to represent the colour of each element
You can:
- Decide which binary digit (or pair of binary digits) corresponds to which colour
You cannot:
- Use one bit for some colours and two for others — you must use either one or two bits for all colours.
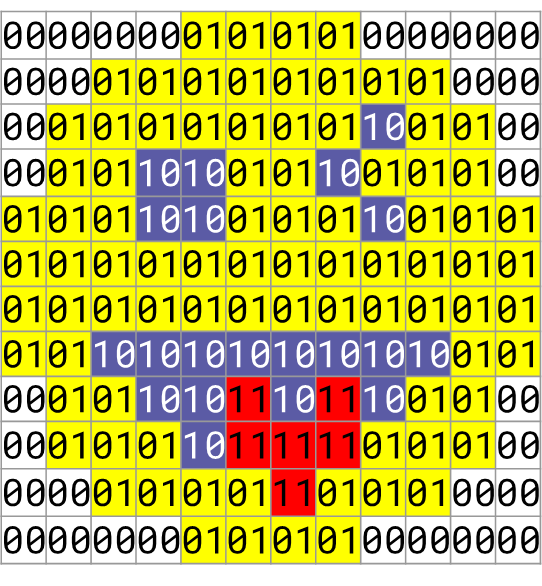
Step 3 – Exchange binary representations to recreate another group’s picture
You need to:
- Include all the information you think the other team need to translate your binary into an actual picture.
111111101010101011111111111010000000101011111111101010101010101111111111001100110011111111110000111111000011111111110000000000111111110010011010100110001111001000010101001000111111110101010101111111111111010101010111111111111101011101011111111111111010111010111111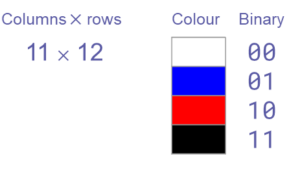
Pixels
Digital images are also composed of individual elements, arranged in a rectangular grid.
The elements of a digital image are called pixels (picture elements).
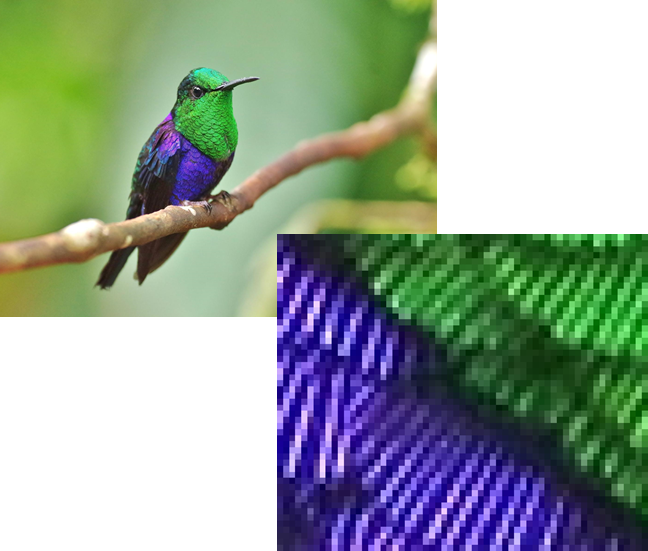

Binary mosaic: reflection
Can you calculate how many bits you used to represent your entire image?
Look at the example on the right:
- There are 14⨉8 = 112 pixels (picture elements).
- I used 1 bit for the colour of each pixel.
- Total number of binary digits for the image:
- 112 pixels ⨉ 1 bit per pixel = 112 bits
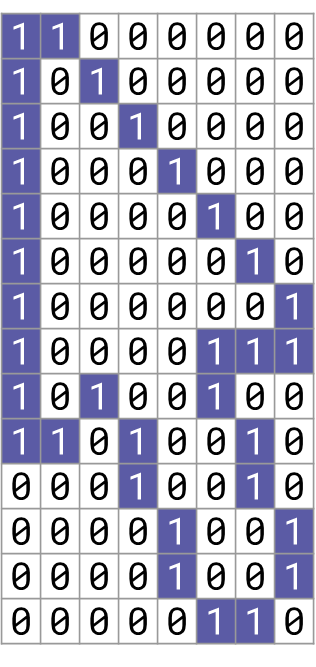
How about this one?
Look at the example on the right:
- There are 10⨉10 = 100 pixels (picture elements).
- I used 2 bits for the colour of each pixel.
- Total number of binary digits for the image:
- 100 pixels ⨉ 2 bits per pixel = 200 bits

Terminology: pixels and resolution
When you made the binary mosaic, you represented an image as a sequence of binary digits.
A digital image is composed of individual elements, arranged in a rectangular grid.
The elements of a digital image are called pixels (picture elements).
The number of pixels in a digital image is the image resolution.
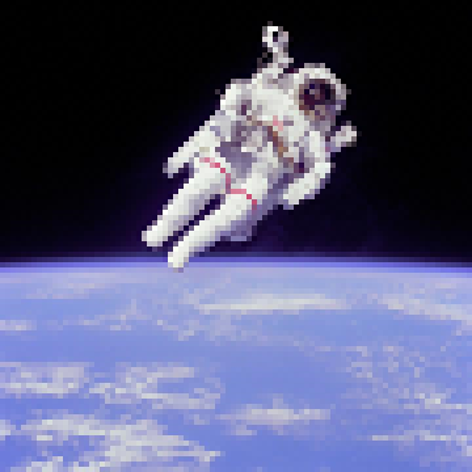
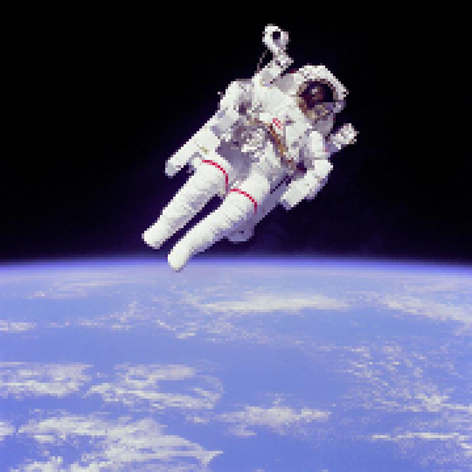
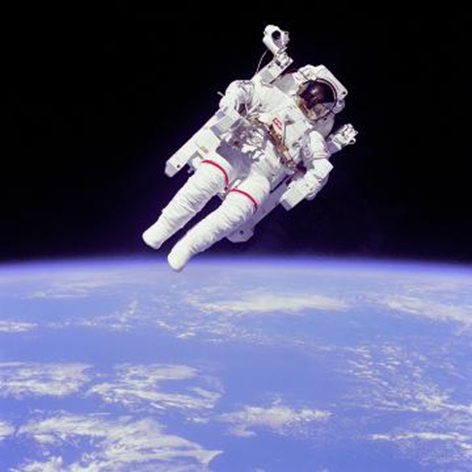
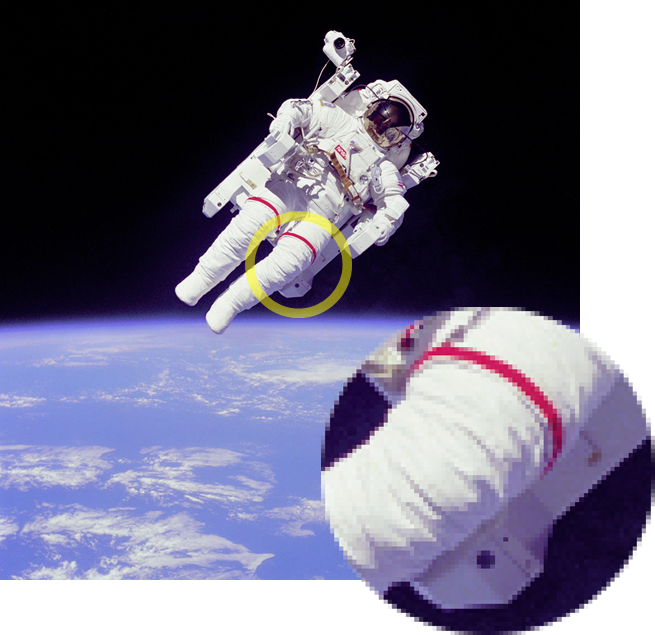



Image representation: resolution trade-offs
Images with high resolution, i.e. a large number of pixels, are:

Terminology: colour depth
For every pixel, a sequence of binary digits represents its colour.
The (fixed) number of binary digits used to represent each pixel’s colour is the colour depth.
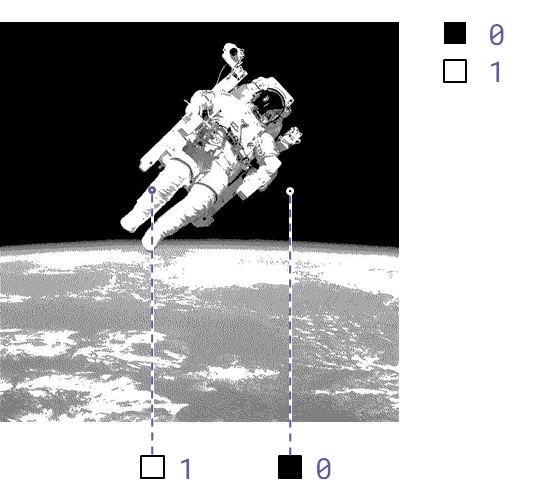
Colour depth: 1 bit (2 possible colours)
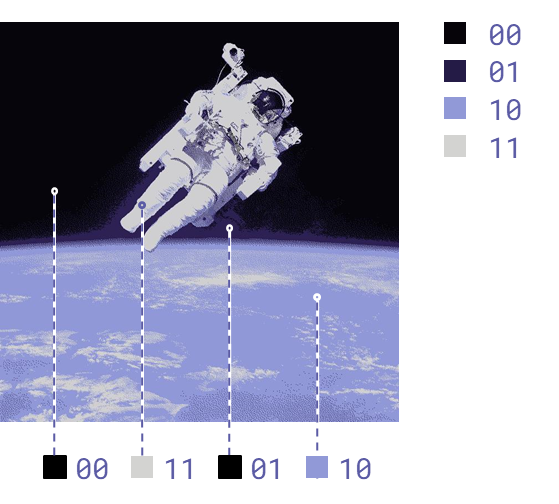
Colour depth: 2 bits (4 possible colours)
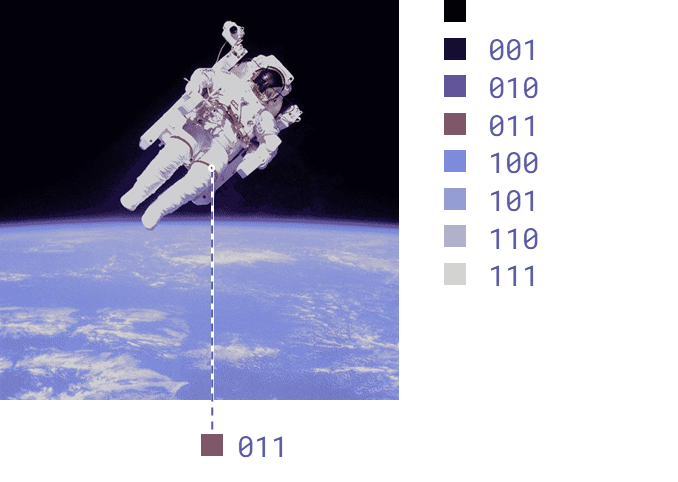
Colour depth: 3 bits (8 possible colours)
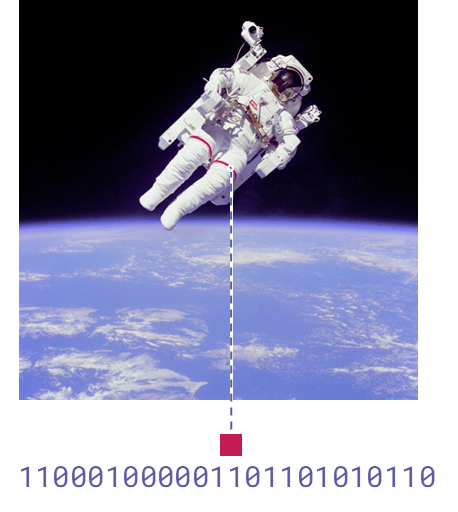
Colour depth: 24 bits
Image representation: colour depth trade-offs
Images with a high colour depth, i.e. a large number of bits representing each pixel’s colour, are:

Terminology
Digital images that are formed using a binary representation of each pixel’s colour are called bitmap images.
Note that there is also an alternative, entirely different approach, called vector graphics. Which we will look at later.

Colour depth: 24 bits
🥈/🥉 Level 2/3 – Pixels
Download the worksheet below and answer the questions, when done upload the completed worksheet to Teams.
🏅 Level Up
🥇 Level 1
- Upload your completed Level 1 – Binary Mosaic worksheet to the Teams assignment.
🥈 Level 2
- Upload your completed Level 2/3 – Pixels worksheet with Task 1 complete to the Teams assignment.
🥉 Level 3
- Upload your completed Level 2/3 – Pixels worksheet with Tasks 1, 2, 3 complete to the Teams assignment.
In this lesson, you…
- Created images out of pixels
- Explored how an image can correspond to a sequence of binary digits and vice versa
- Defined resolution and colour depth
Next lesson, you will…
- Examine how colour can be described as a mixture of red, green, and blue light (RGB colour)
- Calculate the representation size of images