🎯 Learning Objectives
After this lesson you should be able to:
- Write programs that display messages, receive keyboard input, and use simple arithmetic expressions in assignment statements
- Use selection (if-elif-else statements) to control the flow of program execution
- Locate and correct common syntax errors
- Create lists and access individual list items
💬 Key Vocabulary
- Input
- Output
- Variables
- Assignment
- Expressions
- Selection
- Boolean/logical expression (condition)
- List
- Index
- List item
Introduction
In this lesson, you will:
- Brush up on your Python skills
- Use selection (if–elif–else statements) to control the flow of program execution
- You will walk through or write programs that display messages, receive keyboard input, and use arithmetic expressions in assignment statements
- Create lists and access their items
In previous years, you…
- used a text-based programming language (Python) to create programs that involved:
- variables, operators and expressions
- sequence, selection, and iteration

In this unit, you will…
- use Python to develop programs that also involve:
- lists
- strings

📝 Starter Activity
- Let’s see how much Python you remember from Year 7 & 8. Create a new folder on your OneDrive in your Year 9 folder called Advanced Python.
- Download the Word document below into the folder by right clicking and “Save link as…”, then fill out the answers before we go through them as a class.
📝 Selection Recap
- You will be using pair programming, with each member in a pair taking on a specific role:
- Driver: Controls the keyboard and mouse
- Navigator: Provides support and instructions
- You will alternate between roles.

- For this activity you need a selection structure (if-elif-else) when there are multiple branches and your program needs to select which one of them to follow.
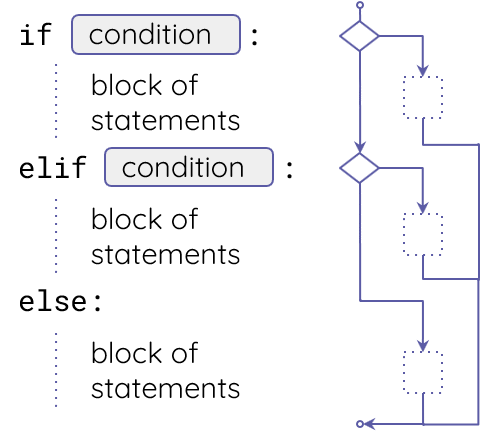
- Let’s extend this program together, to check the day and display whether it’s a weekday on not.
- Copy the code into Thonny.
print("What day is it today?")
day = int(input())Note: The program uses an integer for each day of the week, ranging from 0 for Monday to 6 for Sunday.
📝 Level 1 – How Long Till the Weekend
- Download the Level 1 worksheet to see your task. Then copy the code below into Thonny and complete the task.
print("What day is it today?")
day = int(input())
if day <= 4:
print("It’s a weekday")
remaining =
else:
print("It’s the weekend!")📖 A List of Names
- The names for the days of the week can be stored in a list .
- What is a list? : A comma-separated list of values (items), in square brackets.
- In this example, the list items are strings (i.e. pieces of text), so they need to be in quotation marks.

- A list is a kind of data structure.
- Data structures are organised collections of data.
- In the case of lists, data is organised in a sequence, with each item having a unique index, denoting its position in the list.

- When the program is executed, this is what the list will look like in memory.
- Each item has a unique index, denoting its position in the list. You can see the index of each item on the left from 0 to 6.
📝 Level 2/3 – As Seasons Roll on By
- Download the Level 2/3 worksheet and copy the Python code below into Thonny one task at a time and complete it.
Task 1
months = ["January", "February",
"March", "April", "May",
"June", "July", "August",
"September", "October", "November",
"December"]
print("These are the summer months:")
print(months[ ]) # complete this line
print(months[ ]) # complete this line
print(months[ ]) # complete this lineTask 2
months = ["January", "February",
"March", "April", "May",
"June", "July", "August",
"September", "October", "November",
"December"]
print("What month is it? (1-12)")
month = int(input())
print("It is", months[ ]) # complete this lineTask 3
seasons = ["Winter", "Spring",
"Summer", "Autumn"]
print("What month is it? (1-12)")
month = int(input())
if : # complete this line, type between the if and the :
season = 0
elif : # complete this line
season = 1
elif : # complete this line
season = 2
else:
season = 3
print("It is", seasons[season])🏅 Level Up
🥇 Level 1
- Upload your completed Level 1 worksheet to the Teams assignment.
🥈 Level 2
- Upload your completed Level 2/3 worksheet with Tasks 1 & 2 complete to the Teams assignment.
🥉 Level 3
- Upload your completed Level 2/3 worksheet with Tasks 1, 2, 3 and the Explorer task complete to the Teams assignment.
In this lesson, you…
- Brushed up on your Python skills
- Used selection (if-elif-else statements) to control the flow of program execution
- Created lists and accessed their items
Next lesson, you will…
- Perform operations on lists