🎯 Learning Objectives
- Perform common operations on lists or individual items
💬 Key Vocabulary
- list
- index
- list item
- list operations (append, insert, pop, remove, index, count, reverse, sort, length)
- list membership
- Boolean/logical expression (condition)
Introduction
In this lesson, you will:
- Perform operations on lists
- Brush up on your Python skills (mainly selection)
📖 The Index of an Item
Question
What do you think will be displayed on the screen when this program is executed?

Answer

The number 1 will be displayed.
This is the index of the value “Venus” in the list of planets.
📖 Operations on Lists
There are many operations you can perform on lists and their items.
| Python Code | Description |
|---|---|
| list.append(item) | add item at end of list |
| list.insert(index, item) | add item at index |
| list.pop(index) | remove item at index |
| list.remove(item) | remove item |
| list.index(item) | search for index of item |
| list.count(item) | get occurrences of item |
| list.reverse() | reverse list |
| list.sort() | sort list |
- Examples
- numbers.append(42)
- cities.insert(2, “Oslo”)
- last = values.pop()
- countries.remove(“Japan”)
- where = planets.index(“Mars”)
- nb_the = words.count(“the”)
- values.reverse()
- names.sort()
📝 Level 1/2 – The Solar System
Complete the tasks on the worksheet you can download below to see how our view of the solar system has evolved over time.
To perform the tasks, you will need to perform operations on lists.
Task 1 – Planets
planets = ["Mercury", "Venus",
"Earth", "Mars",
"Jupiter", "Saturn"]
print("Planets in antiquity:")
print(planets)
# Add Uranus to the list
# Add Neptune to the list
# Add Pluto to the list
print("Planets by 1930:")
print(planets)
# Remove Pluto from the list
print("Planets after 2006:")
print(planets)Task 2 – Dwarf Planets
dwarves = # Create list of dwarves
# Change 2nd item to Haumea
# Add Pluto as 2nd item
print("Dwarf planets:")
print(dwarves)📝 Level 3 – Dice Battle Game
- Here is how the Dice Battle game works with an example to help you.
- Roll – The attacker rolls three dice. The defender rolls two.
- Sort – Each player’s rolls are sorted in descending order (highest first).
- Check – Compare the players’ highest roll: lower loses a point.
- Compare the players’ second highest roll: lower loses a point.
- Ties are won by the defender.
Example Game
Roll – The attacker rolls three dice. The defender rolls two.
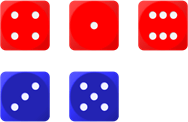
Sort – Each player’s rolls are sorted in descending order (highest first).
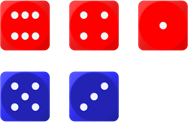
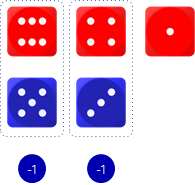
Check – Compare the players’ highest roll: lower loses a point.
Compare the players’ second highest roll: lower loses a point.
Ties are won by the defender.
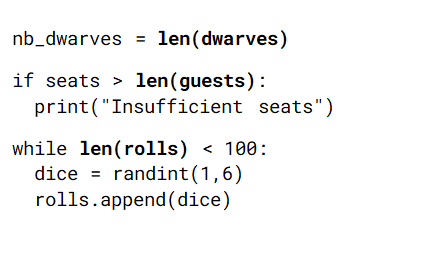
Use the code box below to complete this task. The code will NOT work in Thonny.
📖 Measuring Length
The built-in len function returns the length (number of items) of a list.
Syntax: len(list)
📖 List Membership
The in operator checks if a value is equal to any item in a list.
Expressions formed with in evaluate to either True or False.
Syntax: item in list

Try out the len and in commands by searching through the book Dracula to find out how many words it has and how many times words like “vampire” appear. See if you can change which word you are searching for.
💬 Summary
In this lesson, you…
- Performed operations on lists
- Brushed up on your Python skills (mainly selection)
Next lesson, you will…
- Use iteration (while statements) to control the flow of program execution
- Practise using common operations on lists
- Perform operations on strings
🏅 Level Up
🥇 Level 1
- Upload the Level 1/2 – The Solar System worksheet with Task 1 complete to the assignment on Teams.
🥈 Level 2
- Upload the Level 1/2 – The Solar System worksheet with Task 2 complete to the assignment on Teams.
🥉 Level 3
- Upload the Level 3 – Dice Battle worksheet to the assignment on Teams.