🎯 Learning Objectives
- Describe the meaning of assignment statements
- Use simple arithmetic expressions in assignment statements to calculate values
- Receive input from the keyboard and convert it to a numerical value
💬 Key Vocabulary
- input
- output
- variables
- expressions
- integer
- walk-through
- string
- execution
- operators
📖 Assignment and Expressions
- Assignments are not equations.
- This assignment does not mean that the days variable always equals 365.
- Assignments are instructions to be executed.
- The screenshot on the right is an instruction to assign the value 365 to the days variable.
- A subsequent assignment can assign a new value to the days variable, replacing the previous value.
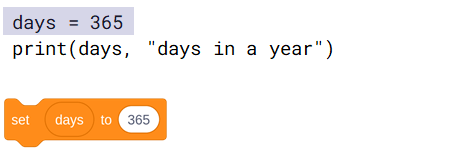
- You can use expressions in assignments.
- This is an instruction to evaluate the expression on the right and then assign the value to the days variable on the left.
- A subsequent assignment can assign a new value to the days variable, replacing the previous value.
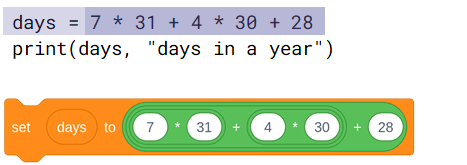
📖 Arithmetic operators (in Python)
You can use these operators to form arithmetic expressions.
| Symbol | Meaning | Examples | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| + | addition | a + 1 | a plus 1 |
| – | difference | b – c | b minus c |
| * | multiplication | 3 * d | 3 times d |
| / | division | 9 / 4 | 9 divided by 4 (value: 2.25) |
| // | integer division | 15 // 2 | quotient of 15÷2 (value: 7) |
| % | remainder of integer division | 15 % 2 | remainder of 15÷2 (value: 1) |
| ** | exponentiation | 2 ** 8 | 2 to the power of 8 (value: 256) |
📖 Referring to Variables
- An expression can refer to the values of variables.
- To evaluate this expression, the days variable must have been assigned a value.
- During program execution, a variable must have been assigned a value before that value is referred to.
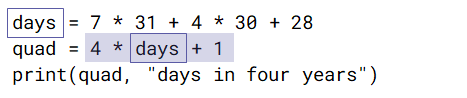
📝 Level 1 – Order Matters
- You will be given a program that is supposed to convert a length of time from seconds to minutes.
- Rearrange (change the order of) the statements, so that the program runs to completion without errors.
📝 Level 2/3 – How to input numbers
Work on programs that receive numerical input from the keyboard and process it.
In this lesson, you…
- Used arithmetic expressions to calculate values
- Used variables to store and reference values
- Followed walk-throughs of code and kept track of variable values
- Wrote programs that receive numerical input from the keyboard
Next lesson, you will…
- Use selection (if statements) to control the flow of program execution
- Introduce elements of randomness into your programs
🏅 Level up
🥇 Level 1
- Complete the Level 1 worksheet and upload it to Teams.
🥈 Level 2
- Complete the Level 2 tasks in the Level 2/3 worksheet and upload screenshots of your code from Thonny to Teams.
🥉 Level 3
- Complete the Level 3 tasks in the Level 2/3 worksheet and upload screenshots of your code from Thonny to Teams.