🎯 Learning Objectives
- Use relational operators to form logical expressions
- Use binary selection (if, else statements) to control the flow of program execution
- Generate and use random integers
💬 Key Vocabulary
- Selection
- relational operators,
- logical (or Boolean) expressions
- conditions
- randomness
- execution
📖 Selection in Python

- Selection is when your programs check conditions and select the path of action that they will follow accordingly.
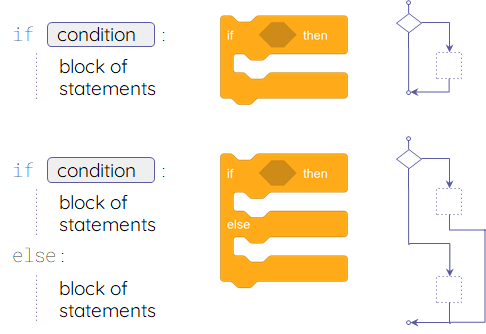
You will need an if or an if, else when there is more than one possible path for your program to follow.
📖 Worksheet – Practise using selection
- Download this lesson’s worksheet to your Home Drive.
📖 Selection example
- The condition will check if the value of
useris equal to the string"Elizabeth". - The expression
user == "Elizabeth"will evaluate to eitherTrueorFalse. - This is the
ifblock, i.e. the code that will be executed if the condition isTrue. - This is the
elseblock, i.e. the code that will be executed if the condition isFalse. - Only one of these blocks will be executed, depending on the value of the condition.

📖 Selection – Syntax Pitfalls
- It’s
ifandelse. No capitals. - A colon : is always required after the
ifcondition and afterelse. - Use indentation to indicate which statements ‘belong’ to the
ifblock and theelseblock. - The
==operator checks for equality. The single=is only used in assignments. useris a variable. Don’t use quotes."Elizabeth"is a string literal. It needs quotes.

📖 Relational operators in Python (comparisons)
You can use these operators to compare the values of expressions.
| Symbol | Meaning | Examples | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| == | equal to | a == 1 | Does a equal 1? |
| != | not equal to | b != c | Are b and c different? |
| < | less than | d < 3 | Is d less than 3? |
| <= | less than or equal to | d <= 3 | Is d at most 3? |
| > | greater than | d > 10 | Is d greater than 10? |
| >= | greater than or equal to | d >= 10 | Is d at least 10? |
- Expressions formed using these operators evaluate to either
TrueorFalse. - You can also use these operators to compare alphanumeric values (strings).
In this lesson, you…
- Used selection (if statements) to control the flow of program execution
- Introduced elements of randomness into your programs
Next lesson, you will…
- Explore how selection can handle more than two possible branches
- Introduce iteration (while statements) to allow the flow of program execution to include loops
🏅 Level up
🥇 Level 1
- Complete the Level 1 – Film Critic task and upload the worksheet to Teams.
🥈 Level 2
- Complete the Level 2 – Lucky Number task and upload the worksheet to Teams.
🥉 Level 3
- Complete the Level 3 – Eligible to Vote task and upload the worksheet to Teams.